70〜80年代を駆け抜けたCPU、AMD「Am2900」:マイクロプロセッサ懐古録(4)(3/4 ページ)
4bit ALUの「Am2901/Am2903」
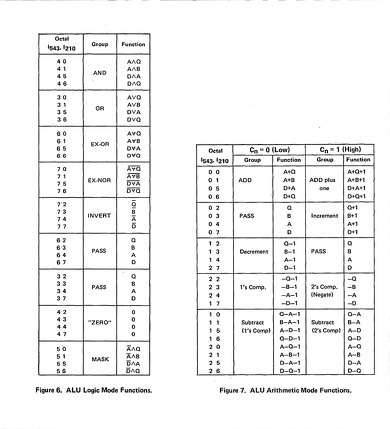
Am2901/Am2903は4bitのALUである。Am2901乗加算のALUで、Am2903はこれに乗算が追加されている。構造的にはこんな形(図4)であり、この当時良くあるAdderなどとそう違いは無かったのだが、一応ALUらしく複数の処理をMicroinstructionの方で選択できるようになっているあたりがAdderとの違いと言える。もっとも、図4左上のDecodeブロックを見れば分かるように、基本ALU Functionは8つしか利用できない。実際にはALU Sourceフィールドまで利用するほか、Logic Mode/Arithmetic Modeというモード切替とCn(Carry)まで使う事で最大116命令(図5の定義を行っている。といっても種別で言えば8種類しか命令が無い訳で、ではこのALUでサポートされていない命令は?というと、そうした機能を持つチップが別に存在する。
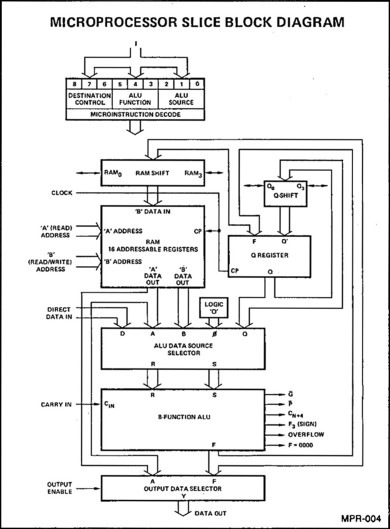 図4:これはAm2901Aのものである。Am2903Aの方には、これにMuxが追加されるだけのはずなのだが、ブロック図を見るとあえて描き方を変えていて、一見するとまるで違う中身のように見えるのが謎[クリックで拡大]
図4:これはAm2901Aのものである。Am2903Aの方には、これにMuxが追加されるだけのはずなのだが、ブロック図を見るとあえて描き方を変えていて、一見するとまるで違う中身のように見えるのが謎[クリックで拡大]あらためて一覧を示すと
| 品番 | 機能 |
|---|---|
| Am2901 | 4bit ALU |
| Am2902 | Look-Ahead Carry Generator |
| Am2903 | 4bit ALU with Hardware Multiply |
| Am2904 | Status and Shift Control Unit |
| Am2905/Am2912 | Bus Transceiver |
| Am2906/Am2907/Am2908 | Bus Transceiver with Parity |
| Am2909/Am2911 | 4bit Address Sequencer |
| Am2910 | Microprogram Controller |
| Am2913 | Priority Interrupt Expander |
| Am2914 | Priority Interrupt Controller |
| Am2915/2916/2917/Am2926/Am2927/ Am2928/Am2929 |
Quad 3-State Bus Transceiver |
| Am2918/Am2919 | Instruction Register |
| Am2920 | Octal D-Type Flip-Flop |
| Am2921 | 1-to-8 Decoder |
| Am2922/Am2923 | Input MUX |
| Am2924 | 3-to-8 Decoder |
| Am2925 | System Clock Generator and Driver |
| Am2930/Am2932 | Main Memory Program Control |
| Am2940 | DMA Generator |
| Am2942 | Programmable Timer/Counter/DMA Generator |
| Am2946/Am2947/Am2948/Am2949 | Octal 3-State Bidirectional Bus Transceiver |
| Am2950/Am2951 | 8-bit Bidirectional I/O Ports |
| Am2954/Am2955 | Octal Registers |
| Am2956/Am2957 | Octal Latches |
| Am2958/Am2959 | Octal Buffers/Line Drivers/Line Receivers |
| Am2960 | Cascadable 16-bit Error Detection and Correction Unit |
| Am2961/Am2962 | 4-bit Error Correction Multiple Bus Buffers |
| Am2964 | Dynamic Memory Controller |
| Am2965/Am2966 | Octal Dynamic Memory Driver |
といった形で多数の周辺チップが用意されており、例えばシフト演算が必要ならAm2904を組み合わせれば良いといった具合だ。あとは扱うデータの幅に応じて、その数だけAm2900シリーズを並べれば良い。4つ並べれば16bit CPUが出来上がる事になる。先のデータシートを読むと、例えばCarry付の16bit乗算を可能にする場合とか、除算を行う場合のアルゴリズム、あるいはメモリ拡張の方法などさまざまなケースの回路例が示されている。今の感覚で言えば、FPGAとかASICで使えるStandard Cell的なもので、これを組み合わせてCPUのコア部を構築。足りないところだけDiscreteで組むかMicroprogramで逃げるか、あるいは完全にソフトウェアで処理するかを決めるという感じになる。
Copyright © ITmedia, Inc. All Rights Reserved.